MAJOR CAUSES OF FEMALE INFERTILITY
There are a number of possible reasons for involuntary childlessness, which makes it all-the-more important to control what you can and take a scientific and methodical approach to help with successful conception. Below we outline the possible reasons for unsuccessful conception, specific to expecting mothers:
Physiological Causes
Ageing
A woman's age is the most significant factor influencing her fertility.
Hormonal Imbalance
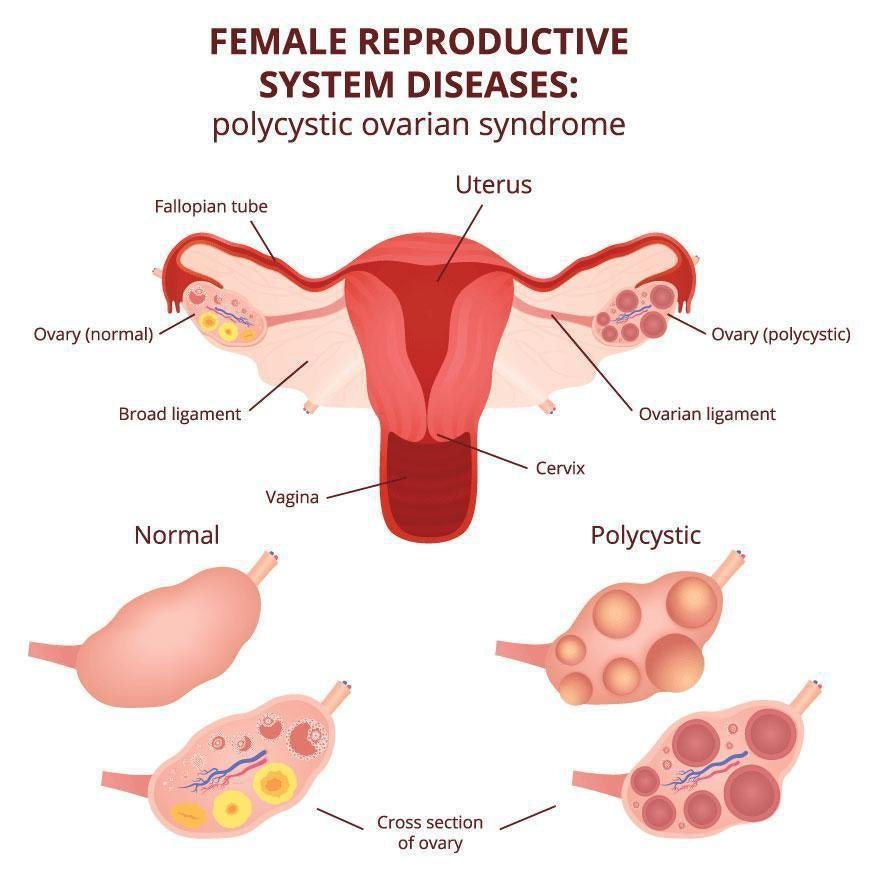
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome(PCOS). PCOS causes a hormone imbalance, which affects ovulation. PCOS is associated with insulin resistance and obesity, abnormal hair growth on the face or body, and acne.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome(PCOS)
-
PCOS is a hormone imbalance which results in disrupted menstrual and ovulation cycles. It is the most common cause of infertility due to anovulation. Anovulation is when the ovaries do not release an oocyte during a menstrual cycle. Therefore, ovulation does not take place.
-
PCOS is a condition characterized by hormonal imbalance, one that tends to interfere with normal ovulation. In addition to ovarian cysts, PCOS is also associated with irregular menstruation, hirsutism (excessive hairiness), obesity, and insulin resistance.
-
An estimated 8-10% of women of reproductive age have PCOS and the majority will experience difficulty in conceiving a child.
Cervical Mucus
-
Insufficient production of fertile-quality cervical mucus could be a contributing cause. This may result from a variety of factors including diet, stress and/ or hormonal issues.
-
The presence of hostile cervical mucus, may also be a contributing cause. This may result from a variety of factors including diet, stress and/ or hormonal issues.
Hypothalamic Dysfunction
Two hormones produced by the pituitary gland are responsible for stimulating ovulation each month — (FSH) and the luteinizing hormone(LH). Excess physical or emotional stress, a very high or very low body weight, or a recent substantial weight gain or loss can disrupt production of these hormones and affect ovulation.
Premature Ovarian Failure
Also called primary ovarian insufficiency, this disorder is usually caused by an autoimmune response or by premature loss of eggs from your ovary (possibly from genetics or chemotherapy). The ovary no longer produces eggs, and it lowers estrogen production in women under the age of 40.
Too Much Prolactin
The pituitary gland may cause excess production of prolactin (hyperprolactinemia), which reduces estrogen production and may cause infertility.
Damage to Fallopian Tubes (Tubal Infertility)
Damaged or blocked Fallopian tubes keep sperm from getting to the egg or block the passage of the fertilized egg into the uterus.
Common conditions that may cause blocked Fallopian tubes are:
-
Endometriosis
-
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
-
Uterine Fibroids
-
Ectopic pregnancy
-
Tubal Ligation Removal
-
Complications from lower abdominal surgery such as Cesarean section
Endometriosis
-
Endometriosis is the development of uterine-lining tissue outside of the uterus. Symptoms may include abdominal pain, heavy periods and infertility.
-
Endometriosis occurs when tissue that normally grows in the uterus implants and grows in other locations. This extra tissue growth — and the surgical removal of it — can cause scarring, which may block Fallopian tubes and keep an egg and sperm from uniting.
-
Endometriosis can also affect the lining of the uterus, disrupting implantation of the fertilized egg. Endometriosis is found in about 35 percent of infertile women who have laparoscopy as part of their infertility assessment.

Uterine or Cervical Causes
Uterine or cervical causes can impact fertility by interfering with implantation or increasing the likelihood of a miscarriage:
-
Benign polyps or tumors (fibroids or myomas) are common in the uterus. Some can block Fallopian tubes or interfere with implantation, affecting fertility.
-
Endometriosis scarring or inflammation within the uterus can disrupt implantation.
-
Uterine abnormalities present from birth, such as an abnormally shaped uterus, can cause problems becoming or remaining pregnant.
-
Cervical stenosis, a narrowing of the cervix, can be caused by an inherited malformation or damage to the cervix.
-
Sometimes the cervix can't produce the best type of mucus to allow the sperm to travel through the cervix into the uterus.

Unexplained Infertility
Sometimes, the cause of infertility is never found. A combination of several minor factors in both partners could cause unexplained fertility problems.
It is vitally important that any couples suffering from involuntary childlessness, seek to consult a fertility specialist initially, to confirm, that there are not any physiological factors in either the male or female, which are contributing to unsuccessful conception, in order to have all information at your disposal.
Lifestyle & Behavioral Factors
- Stress
- Medication
- Poor or inadequate nutrition
- Alcohol consumption
- Smoking
Environmental Factors
- Environmental pollutants
- Toxins
- Excess Heat
Causes of Infertility in Men
Fertility disorders in both women & men may also be partly attributed to our own physiology. Below we explore some of the medical conditions which may also make successful conception more difficult to achieve.
Organic causes of fertility disorders in men:
- Age
- Undescended testes
- Varicose veins in the testicles
- Impaired testicle function, post-infection
- Changes to hereditary factors
- Hormonal disorders
We encourage all of our customers to take our no-obligation/ free-of-charge online fertility evaluation, where one of our fertility specialists will analyse your particular case, and make recommendations, specific to your situation.